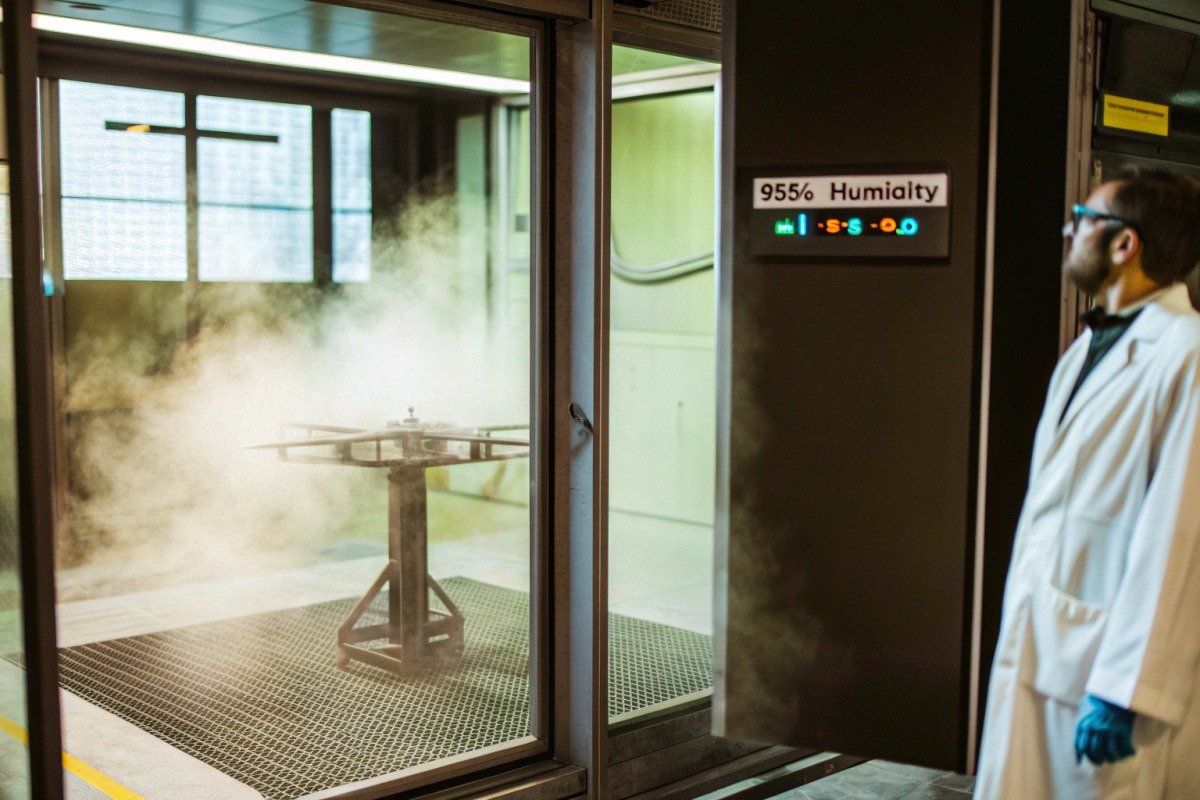
When our engineering team first encountered a returned firefighting drone with corroded PCB traces, the failure told us everything quality control protocols 1. The drone had operated in 95% humidity during a wildfire suppression mission. Its electronics failed within weeks. This problem costs operators thousands in repairs and downtime.
To verify corrosion resistance of firefighting drone electronics, request testing certifications like MIL-STD-810, IEC 60068-2, and ASTM B117. Inspect conformal coating specifications, IP67+ ratings, and accelerated life testing data. Review manufacturer quality control protocols for humidity cycling and salt spray tests.
Below, we break down the exact steps to ensure your firefighting drone electronics survive extreme conditions. Each section gives you practical verification methods you can apply immediately.
What testing certifications should I request to confirm my firefighting drone's electronics are truly corrosion-resistant?
Our quality control lab runs dozens of certification tests each month. Many buyers ask for certificates without knowing what they actually prove. The wrong certification gives false confidence. The right one saves your investment.
Request MIL-STD-810 for environmental extremes, IEC 60068-2-30 for humidity cycling, ASTM B117 for salt spray resistance, and RTCA DO-160 for aviation-grade durability. These standards test electronics under conditions matching firefighting environments up to 200°C and 100% relative humidity.
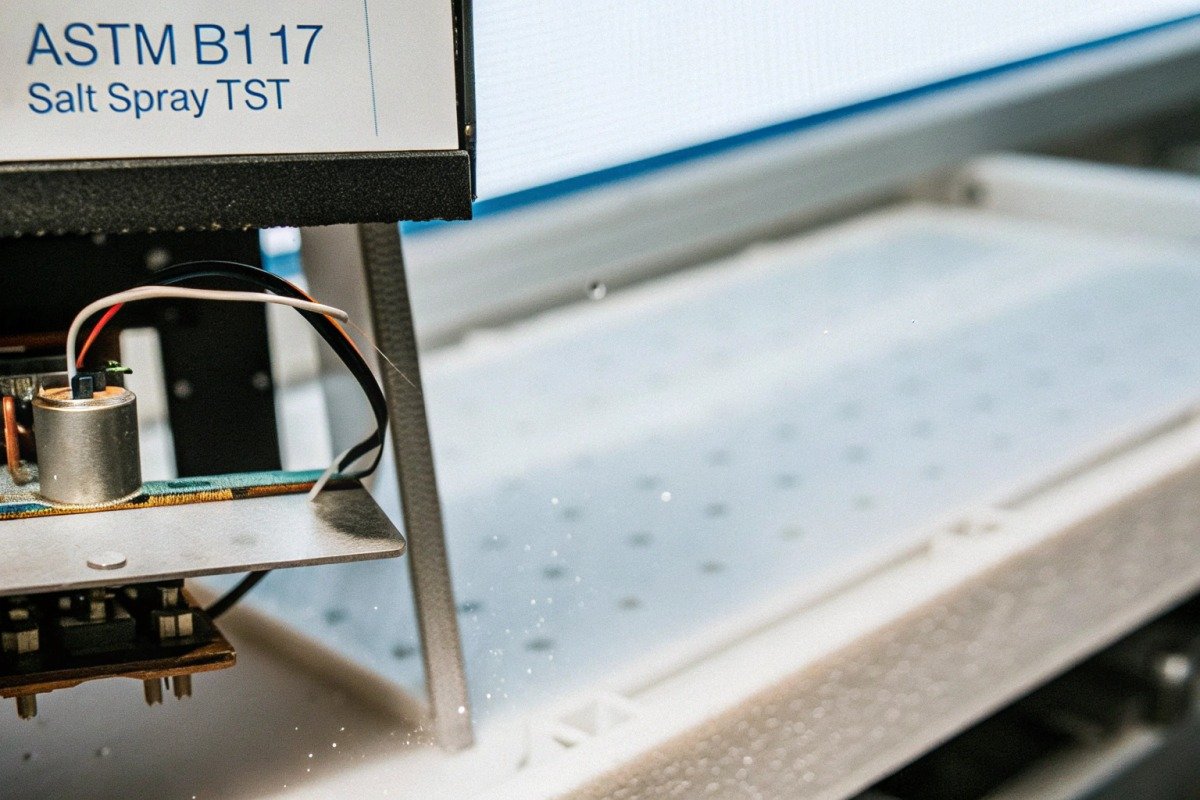
Understanding Key Testing Standards
Not all certifications carry equal weight for firefighting applications. MIL-STD-810 2 originated from military requirements. It tests equipment under extreme temperature, humidity, salt fog, and chemical exposure. For drones entering fire zones, this standard matters most.
IEC 60068-2 covers environmental testing procedures. Section 2-30 specifically addresses damp heat cycling. This test exposes electronics to alternating high humidity and temperature cycles. It reveals weaknesses in conformal coatings and solder joints that single-condition tests miss.
ASTM B117 3 remains the industry standard for salt spray testing. While firefighting drones don't typically encounter ocean salt, this test accelerates corrosion mechanisms. It predicts long-term performance in humid, contaminated environments.
Certification Comparison Table
| Certification | Primary Test Conditions | Duration | Relevance to Firefighting |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIL-STD-810H | -40°C to +71°C, 95% RH, salt fog | 500+ hours | High – covers extreme heat and humidity |
| IEC 60068-2-30 | 25-55°C cycling, 95% RH | 6-12 cycles | High – tests coating integrity |
| ASTM B117 | 35°C, 5% salt solution spray | 96-1000 hours | Medium – accelerated corrosion |
| RTCA DO-160G | Multiple environmental categories | Varies | High – aviation reliability standard |
| IP67/IP68 | Dust and water immersion | 30 min at 1m depth | Medium – enclosure protection only |
What Certifications Often Miss
Standard certifications don't always replicate firefighting conditions. Fire zones produce acidic combustion byproducts. Smoke contains corrosive chemicals that standard salt spray tests ignore. When we design our firefighting drones, we add custom tests that expose electronics to simulated smoke residues and ash contamination.
Ask manufacturers if they conduct supplementary testing beyond standard certifications. Request documentation showing tests with combustion byproducts or high-temperature humidity combinations above 85°C.
How can I verify that the internal PCB coatings will withstand extreme humidity during high-temperature operations?
During our production runs, we test every batch of conformal coatings before application. A coating that works at room temperature often fails at 150°C. Moisture penetrates through microscopic pinholes. Your electronics die from the inside out.
Verify PCB coatings by requesting coating type specifications (Parylene, silicone, or polyurethane), thickness measurements (25-75 microns), adhesion test results per ASTM D3359, and accelerated aging data showing performance after 1000+ hours at 85°C/85% RH conditions.
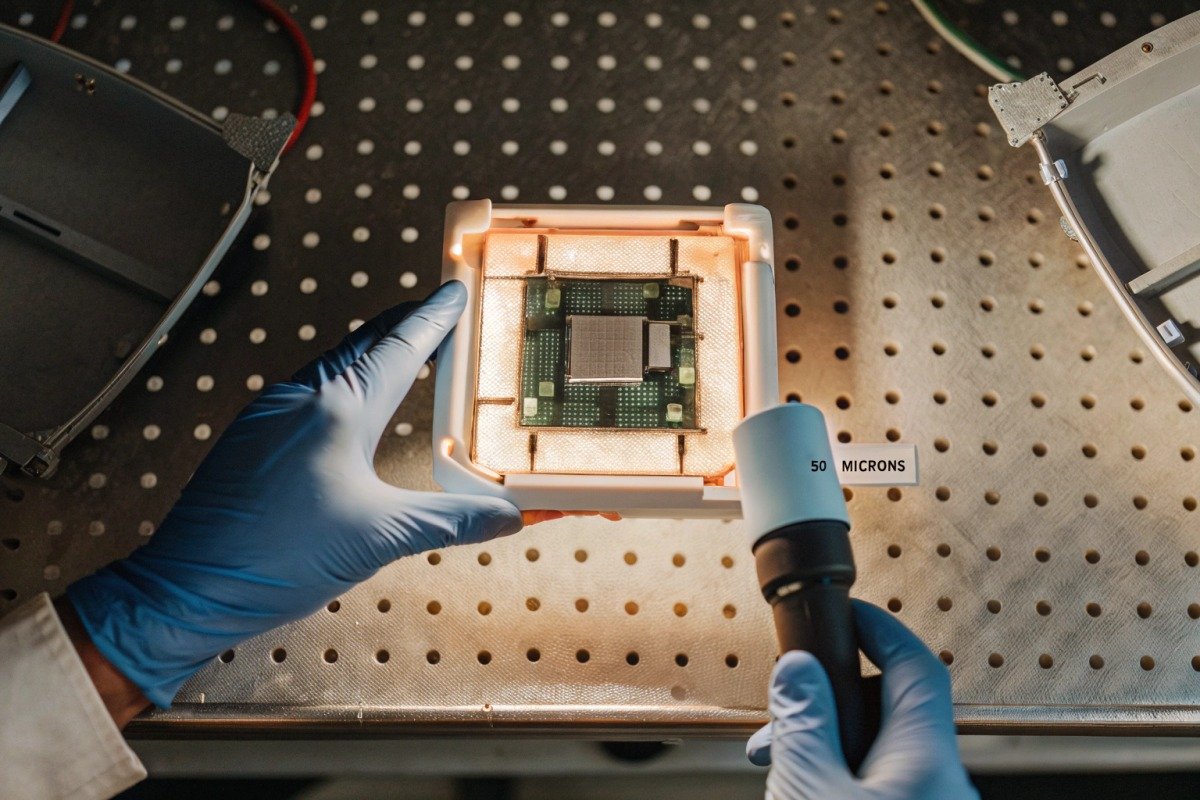
Types of Conformal Coatings and Their Performance
Each coating type offers different protection levels. Parylene 4 provides the best moisture barrier but costs more. Silicone handles temperature extremes well. Polyurethane offers chemical resistance. Acrylic is cheapest but fails fastest in high heat.
For firefighting applications, our engineering team recommends Parylene or silicone coatings. These maintain integrity above 150°C while blocking moisture ingress. Acrylic coatings become brittle and crack at temperatures above 125°C.
Conformal Coating Performance Comparison
| Coating Type | Max Operating Temp | Moisture Resistance | Chemical Resistance | Cost Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parylene C | 150°C continuous | Excellent | Good | High |
| Silicone | 200°C continuous | Very Good | Good | Medium-High |
| Polyurethane | 130°C continuous | Good | Excellent | Medium |
| Acrylic | 125°C continuous | Fair | Poor | Low |
| Epoxy | 150°C continuous | Good | Very Good | Medium |
Verification Methods for Coating Quality
Request cross-section microscopy images showing coating thickness uniformity. Uneven coatings create weak spots where moisture enters. Ask for electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) data that measures coating barrier properties over time.
Thermal cycling test results reveal coating adhesion under stress. When electronics heat rapidly during operation, coatings expand at different rates than PCB substrates. Poor adhesion causes delamination. Good coatings survive 1000 thermal cycles from -40°C to +125°C without cracking.
PCB Surface Finish Considerations
The surface finish beneath the coating matters equally. Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold (ENIG) 5 provides excellent corrosion resistance at solder joints. Organic Solderability Preservatives (OSP) cost less but degrade faster in humidity.
When reviewing manufacturer specifications, check both the conformal coating type and the underlying PCB finish. ENIG with Parylene coating creates the most robust protection for firefighting environments.
What specific engineering data should I look for to ensure my drone's components won't fail in harsh environments?
When we qualify new suppliers for electronic components, we require complete engineering data packages. Surface-level specifications hide critical weaknesses. The detailed data tells the real story of how components behave under stress.
Look for accelerated life testing (ALT) reports showing mean time between failures (MTBF) above 10,000 hours, thermal analysis data, humidity cycling curves, galvanic corrosion assessments for dissimilar metals, and failure mode analysis documenting exactly how components degrade under stress.

Critical Engineering Data Points
MTBF data quantifies reliability. mean time between failures (MTBF) 6 However, test conditions matter more than the number itself. An MTBF of 50,000 hours tested at 25°C tells you nothing about performance at 150°C. Request MTBF data specifically tested under high-temperature, high-humidity conditions.
Thermal analysis shows heat distribution across circuit boards. Hot spots accelerate corrosion. Components near heat sources need extra protection. Ask for thermal imaging data taken during maximum power operation.
Engineering Data Checklist
| Data Type | What It Reveals | Acceptable Range | Red Flags |
|---|---|---|---|
| MTBF at 85°C/85% RH | Reliability under stress | >10,000 hours | Data only at room temperature |
| Thermal imaging | Heat distribution | <100°C at components | Hot spots >120°C |
| Humidity cycling curves | Coating performance over time | <5% impedance change | Rapid degradation after 500 hours |
| Galvanic compatibility | Metal pairing risks | Compatible pairs listed | Copper-aluminum direct contact |
| Failure mode analysis | How components fail | Gradual degradation | Sudden catastrophic failures |
Understanding Failure Modes
Different failure modes require different prevention strategies. Gradual resistance increase from oxidation allows monitoring and prediction. Sudden connector failures from galvanic corrosion 7 cause unexpected system shutdowns.
Request documentation showing the primary failure modes for each critical component. Our design team uses this information to select redundant systems and maintenance intervals. A drone with known failure modes is safer than one with unknown weaknesses.
Material Selection Documentation
Dissimilar metals in contact create galvanic cells that accelerate corrosion. Aluminum and copper junctions corrode rapidly in humid conditions. Steel fasteners in aluminum housings create similar problems.
Ask for material compatibility assessments. Good manufacturers document every metal-to-metal interface and the protection methods used. Sacrificial anodes, isolating gaskets, and compatible alloy selections prevent galvanic corrosion.
Battery terminals deserve special attention. High current connections generate heat and attract moisture. Corroded battery terminals cause sudden power loss during critical operations. Verify that battery connection designs include corrosion-resistant plating and sealed enclosures.
How do I evaluate a manufacturer's internal quality control process for testing electronic durability in humid conditions?
During factory audits from our overseas partners, the quality control area reveals everything. Clean testing equipment and documented procedures indicate serious commitment. Dusty chambers and missing records suggest corner-cutting. Your evaluation determines whether certificates reflect reality.
Evaluate manufacturers by requesting facility tours or video walkthroughs of environmental test chambers, reviewing calibration records for testing equipment, examining sample sizes and acceptance criteria in test protocols, and verifying that incoming component inspection includes humidity-related parameters.

Key Quality Control Processes to Verify
Environmental test chambers require regular calibration. Temperature and humidity sensors drift over time. Uncalibrated equipment produces unreliable test results. Ask for calibration certificates dated within the past 12 months.
Sample size matters for statistical validity. Testing one unit from a batch of 1000 proves nothing. Proper quality control tests statistically significant samples. For critical components, destructive testing of multiple units per batch ensures consistent quality.
Quality Control Evaluation Framework
| QC Element | Good Practice | Warning Signs | How to Verify |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test chamber calibration | Annual third-party calibration | No records or expired certificates | Request calibration certificates |
| Sample sizes | AQL-based sampling per ISO 2859 | Single unit testing per batch | Review test protocols |
| Incoming inspection | Moisture sensitivity level checks | Visual inspection only | Ask for incoming QC procedures |
| Documentation | Complete traceability | Missing batch records | Request sample batch file |
| Personnel training | Certified test operators | Untrained staff running tests | Ask for training records |
Understanding Accelerated Life Testing Protocols
Accelerated life testing 8 (ALT) compresses years of field operation into weeks of laboratory testing. Proper ALT combines multiple stress factors simultaneously. Temperature, humidity, and vibration applied together reveal failures that single-stress tests miss.
Ask how manufacturers correlate accelerated test results to field performance. Good manufacturers track field returns and compare them to predicted failure rates from ALT. This feedback loop improves test protocol accuracy over time.
Supplier Audit Considerations
If possible, visit the manufacturing facility or request a video walkthrough. Observe the environmental test area specifically. Look for multiple test chambers capable of different temperature and humidity ranges. Check whether test equipment appears well-maintained and actively used.
Ask operators about their test procedures. Knowledgeable staff can explain why specific test parameters were chosen. Vague answers suggest procedures exist only on paper.
Our quality team maintains detailed incoming inspection protocols for every component. We share these protocols with customers who request them. Transparent manufacturers welcome quality discussions. Defensive responses to quality questions indicate potential problems.
Post-Production Verification
Quality control extends beyond production. Good manufacturers conduct ongoing reliability testing on production samples. They track field failure data and investigate root causes.
Request field failure rate data for similar products. Manufacturers with low failure rates have proven quality systems. Those unwilling to share this data may be hiding problems.
Conclusion
Verifying corrosion resistance requires checking certifications, coating specifications, engineering data, and quality control processes. Request documented proof for each element. Your due diligence today prevents expensive failures tomorrow.
Footnotes
1. SixSigma.us provides an overview of quality control in manufacturing and best practices. ↩︎
2. Wikipedia provides a comprehensive overview of the MIL-STD-810 standard and its applications. ↩︎
3. Official ASTM International standard for operating salt spray (fog) apparatus. ↩︎
4. SCS Coatings, a leading provider, details the properties and types of Parylene coatings. ↩︎
5. Sierra Circuits, an industry expert, explains ENIG PCB surface finish and its benefits. ↩︎
6. IBM provides a clear definition and explanation of Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF). ↩︎
7. The Association for Materials Protection and Performance (AMPP) explains galvanic corrosion. ↩︎
8. Wikipedia offers a good overview of accelerated life testing methodology and purpose. ↩︎


