When our engineering team first developed multispectral camera integration protocols 1, we watched farmers struggle with mismatched sensors and incompatible software. The frustration of investing thousands in equipment that fails to deliver actionable crop data 2 is real. This guide addresses those exact pain points.
To select and integrate multispectral cameras for agricultural drones, prioritize sensors with red-edge and near-infrared bands, verify hardware and software compatibility with your drone platform, work directly with manufacturers for customization options, and ensure comprehensive technical support including calibration services and spare parts availability.
The sections below break down each critical decision point. We will cover sensor specifications, compatibility verification, customization possibilities, and support services. Let’s dive into the details that matter most for your operation.
Which multispectral sensor specifications should I prioritize for high-precision crop health mapping?
Our production facility tests dozens of multispectral sensors each year. Many buyers focus only on price. They overlook the specifications that actually determine mapping accuracy. This oversight leads to disappointing results and wasted investment.
For high-precision crop health mapping, prioritize sensors with at least five spectral bands including red-edge and near-infrared, image resolution of 3.5 inches per pixel or better, global shutter technology for distortion-free capture, and geo-tagging capability for consistent data across multiple flight missions.
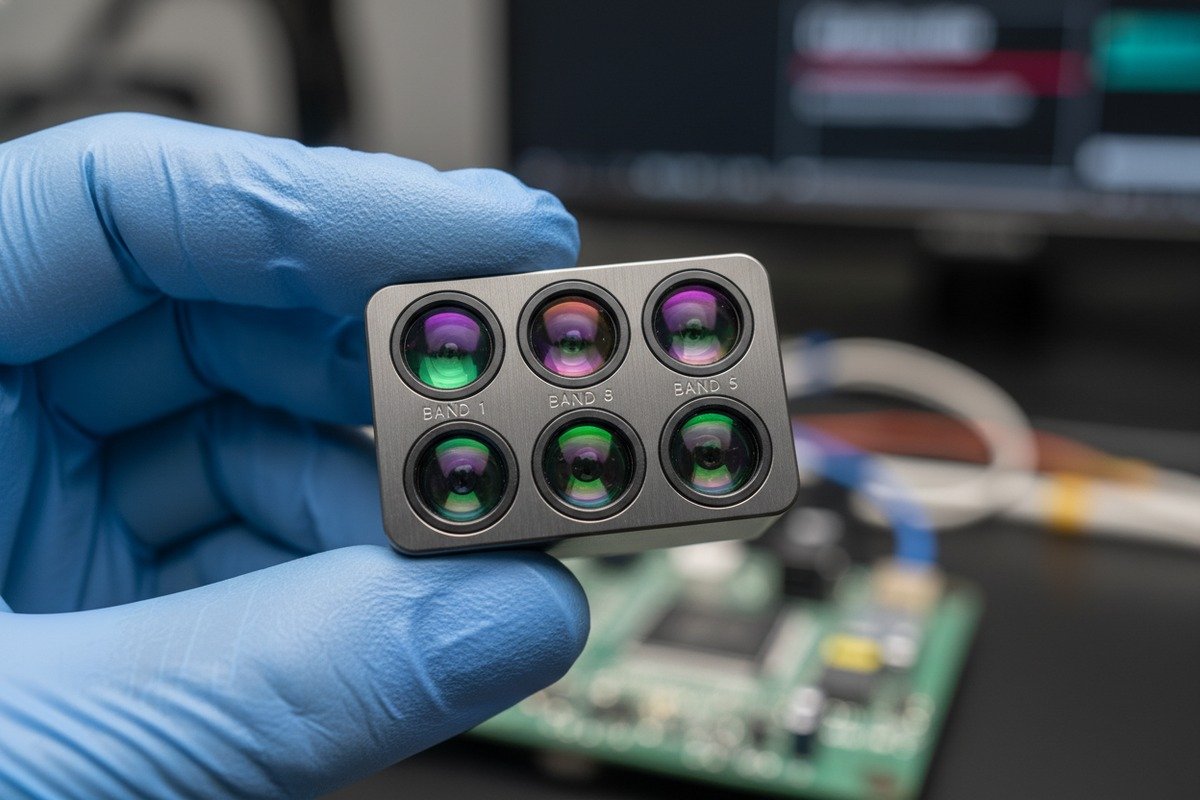
Understanding Spectral Bands and Their Functions
Different spectral bands reveal different information about your crops. A basic 3-band system captures green, red, and near-infrared wavelengths. This setup works for general health assessment. However, 5-band systems add blue and red-edge bands. five spectral bands 3 The red-edge band is particularly valuable. It detects plant stress before visible symptoms appear.
| Band Type | Wavelength Range | Primary Agricultural Use |
|---|---|---|
| Blue | 450-495 nm | Chlorophyll detection, soil-plant differentiation |
| Green | 495-570 nm | Plant vigor assessment, peak vegetation reflectance |
| Red | 620-750 nm | Chlorophyll absorption, vegetation indices |
| Red-Edge | 700-730 nm | Early stress detection, nitrogen content estimation |
| Near-Infrared | 750-1400 nm | Biomass calculation, water content analysis |
Resolution Requirements by Farm Size
Image resolution directly impacts your ability to identify problems early. Our engineers have found that resolution needs vary by operation scale. For farms under 500 acres, 3.5 inches per pixel provides excellent detail. This resolution can identify individual weed patches within crop rows. Larger operations may accept slightly coarser resolution to improve flight efficiency.
Global Shutter vs. Rolling Shutter
Global shutter technology 4 captures all pixels simultaneously. Rolling shutter captures line by line. This difference matters during flight. Rolling shutter creates distortion when the drone moves. Global shutter eliminates this problem entirely. For agricultural mapping, global shutter is essential. It ensures your data remains consistent across different flight conditions.
Geo-tagging and Time-stamping Features
Precision agriculture 5 requires tracking changes over time. Every image needs accurate location data. Geo-tagging embeds GPS coordinates into each image file. Time-stamping records exactly when each image was captured. Together, these features enable meaningful comparisons between flights. Without them, you cannot track crop development or measure treatment effectiveness.
How do I verify that the multispectral camera is fully compatible with my drone's existing software and hardware?
In our experience exporting to the US and European markets, compatibility issues cause more returns than any other problem. Buyers assume cameras work universally. They do not. Each drone platform has specific requirements. Verification before purchase saves significant time and money.
Verify multispectral camera compatibility by checking physical mounting options, confirming power supply requirements match your drone's output, ensuring gimbal stabilization support, testing data processing software integration, and reviewing firmware compatibility with your flight controller.

Physical Integration Requirements
The camera must physically fit your drone. This sounds obvious. Yet many buyers overlook mounting dimensions and weight distribution. Heavier sensors like the MicaSense RedEdge-P require larger platforms. Compact options like the DJI Mavic 3M integrate into smaller drones. Check the following specifications before purchasing:
| Compatibility Factor | What to Check | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Camera weight vs. drone payload capacity | Exceeding payload reduces flight time and stability |
| Mounting | Available mounting points and adapters | Improper mounting causes vibration and image blur |
| Power | Camera voltage requirements vs. drone output | Voltage mismatch damages equipment |
| Data Connection | Communication protocols (USB, HDMI, serial) | Incompatible protocols prevent data transfer |
| Gimbal | Gimbal load capacity and control integration | Stabilization quality affects image usability |
Software Compatibility Verification
Raw multispectral data requires specialized processing software. Pix4D is the industry standard. However, not all cameras integrate equally well. Some require additional plugins. Others need manual calibration settings. Before buying, confirm your camera works with your preferred software.
When we calibrate our flight controllers, we always test data export formats. Your camera should output standard formats like GeoTIFF or JPEG with embedded metadata. Proprietary formats create processing headaches. They may lock you into specific software ecosystems.
Firmware and Flight Controller Integration
Modern agricultural drones rely on sophisticated flight controllers. Your multispectral camera must communicate with this system. It should trigger automatically at predetermined intervals. It should adjust settings based on flight altitude. Some cameras support RTK/PPK positioning 6 for centimeter-level accuracy. Verify these features work with your specific drone model.
Testing Before Full Deployment
Request a trial period or demonstration before committing to purchase. A reputable supplier will support this request. During testing, fly your actual routes. Process the resulting data. Evaluate image quality, geo-referencing accuracy, and software integration. This hands-on verification prevents costly surprises after purchase.
Can I collaborate with my manufacturer to customize multispectral camera integration for my specific agricultural needs?
Our development team works with clients daily on custom integration projects. Many buyers do not realize this option exists. They accept off-the-shelf limitations. However, customization often solves specific operational challenges that generic solutions cannot address.
Yes, reputable manufacturers offer collaborative customization for multispectral camera integration, including custom mounting solutions, tailored software workflows, specific spectral band configurations, integration with existing farm management systems, and OEM branding options for resellers.

Types of Customization Available
Customization ranges from simple modifications to complete system redesigns. Our engineering team categorizes options into three levels. Understanding these levels helps you communicate effectively with potential suppliers.
| Customization Level | Examples | Typical Timeline | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | Custom mounting brackets, branded labeling, accessory bundles | 1-2 weeks | Low |
| Intermediate | Modified gimbal systems, custom software presets, integrated sensors | 4-8 weeks | Moderate |
| Advanced | Custom spectral band selection, proprietary data processing, autonomous operation modes | 3-6 months | High |
The Collaborative Development Process
Effective customization requires clear communication. Start by documenting your specific needs. What crops do you monitor? What problems do you need to detect? What software do you currently use? This information guides engineering decisions.
We begin every custom project with a detailed requirements document. We then propose solutions and review them with clients. Prototyping follows approval. Testing ensures the final product meets specifications. This structured approach prevents misunderstandings and delays.
Integration with Existing Farm Systems
Modern precision agriculture involves multiple data sources. Your multispectral drone should integrate with ground sensors, irrigation systems, and farm management software. farm management systems 7 Custom integration makes this possible. It connects drone-acquired data with broader agricultural data ecosystems.
Edge computing capabilities represent an emerging customization option. Some drones can process multispectral data in real-time during flight. This eliminates extensive post-flight analysis. You receive actionable insights immediately. Custom AI algorithms can identify specific pests, diseases, or environmental stresses unique to your crops.
OEM and Branding Options for Resellers
For distributors and dealers, OEM customization adds significant value. We offer custom branding on hardware and software interfaces. Packaging reflects your company identity. Documentation carries your logos and contact information. These options help resellers build their own brand while leveraging proven technology.
What technical support and calibration services will my supplier provide for my multispectral imaging system?
When we onboard new clients, support questions arise immediately. Technical support separates reliable suppliers from problematic ones. Your multispectral system requires ongoing maintenance. Calibration affects data accuracy. Parts availability affects uptime. These factors determine your long-term success.
Comprehensive supplier support for multispectral imaging systems should include initial calibration services, remote troubleshooting assistance, firmware update support, spare parts availability with reasonable delivery times, on-site technical training options, and documentation for regulatory compliance in your operating region.

Calibration Requirements and Services
Multispectral cameras require regular calibration. Sensors drift over time. Environmental factors affect accuracy. Proper calibration ensures your vegetation indices remain meaningful. Most systems need calibration every 50-100 flight hours. Some require calibration before each flight using reference panels.
Your supplier should provide:
- Initial factory calibration with documentation
- Field calibration tools and procedures
- Recalibration services at reasonable intervals
- Calibration verification methods
Remote and On-Site Technical Support
Problems will occur. Firmware glitches, hardware failures, and software conflicts happen to every operator. Your supplier's response capability determines how quickly you return to productive operation. We maintain dedicated support teams across multiple time zones. This ensures timely assistance regardless of your location.
| Support Type | What to Expect | Response Time Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Email Support | Detailed technical guidance, documentation | 24-48 hours |
| Phone Support | Real-time troubleshooting, urgent issues | Same business day |
| Remote Desktop | Software configuration, firmware updates | Scheduled appointment |
| On-Site Service | Hardware repair, training, complex integration | 1-2 weeks advance scheduling |
| Parts Delivery | Replacement components, consumables | 3-7 business days |
Spare Parts and Repair Services
Multispectral cameras contain precision components. Filters, lenses, and sensors can suffer damage. Propeller strikes happen. Environmental exposure degrades materials. A reliable supplier maintains parts inventory. They provide clear pricing and reasonable delivery times.
Ask potential suppliers these questions:
- What spare parts do you stock?
- What are typical delivery times to my region?
- What is your repair turnaround time?
- Do you offer advance replacement programs?
Training and Documentation
Operating multispectral systems requires specific knowledge. Your supplier should provide comprehensive training. This includes hardware operation, software workflows, and data interpretation. Documentation supports ongoing learning. It should cover equipment operation, troubleshooting procedures, and maintenance schedules.
Regulatory Compliance Support
Different regions have different drone regulations 8. Your supplier should understand requirements in your operating area. They should provide necessary certifications and documentation. This includes safety certifications, radio frequency compliance, and import documentation. For our US and European clients, we ensure all required certifications accompany shipments.
Conclusion
Selecting and integrating multispectral cameras requires attention to specifications, compatibility, customization options, and support services. Prioritize sensors with appropriate spectral bands. Verify integration before purchase. Explore customization possibilities. Ensure comprehensive support availability. These steps lead to successful precision agriculture implementation.
Footnotes
1. Replaced with a page discussing multispectral sensors on agricultural drones and their integration with specialized agriculture software. ↩︎
2. Discusses how drones provide actionable insights for crop management decisions. ↩︎
3. Details the common five spectral bands used in agricultural multispectral cameras. ↩︎
4. Explains how global shutter technology eliminates distortion in drone imaging. ↩︎
5. Provides a definition and overview of precision agriculture from a government source. ↩︎
6. Compares RTK and PPK positioning methods for achieving high accuracy in drone mapping. ↩︎
7. Discusses the integration and benefits of farm management systems in modern agriculture. ↩︎
8. Provides official FAA regulations for agricultural drone operations and dispensing substances. ↩︎


